Scientists Lay Foundation for Gene-Editing Therapy for Late-Onset Tay-Sachs
NIH scientists successfully reduced the severity of late-onset Tay-Sachs (LOTS) disease in human cell cultures and a mouse model using a novel gene-editing treatment. LOTS is a rare form of Tay-Sachs disease, with signs and symptoms such as muscle weakness, loss of coordination, muscle spasms and sometimes loss of mental function beginning in late childhood to adulthood.
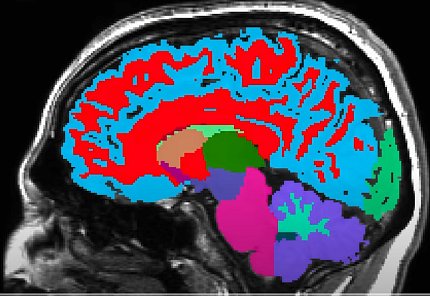
Researchers Develop New Brain Scanner
A scientific team supported in part by NIH has developed a new, ultra-high-resolution brain imaging system that can reconstruct microscopic brain structures that are disrupted in neurological and neuropsychiatric brain disorders. The new system is a significant advance over conventional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanners that cannot visualize these tiny but clinically important structures.