First Patient-Derived Stem Cell Model Developed for Eye Conditions Related to Albinism
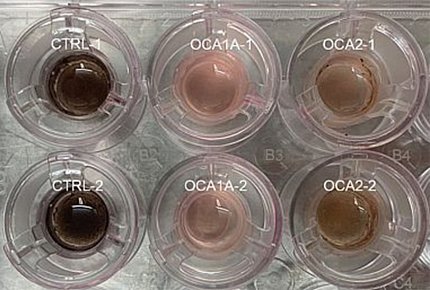
Photo: NEI
Researchers at NEI have developed the first patient-derived stem cell model for studying eye conditions related to oculocutaneous albinism (OCA).
“This ‘disease-in-a-dish’ system will help us understand how the absence of pigment in albinism leads to abnormal development of the retina, optic nerve fibers and other eye structures crucial for central vision,” said Dr. Aman George, a staff scientist in the NEI Ophthalmic Genetics and Visual Function Branch, and lead author of a report describing the model’s development.
Stem Cell Reports published the article in its January edition.

OCA is a set of genetic conditions that affects pigmentation in the eye, skin and hair due to mutation in the genes crucial to melanin pigment production.
In the eye, pigment is present in the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE), and aids vision by preventing the scattering of light. The RPE is located right next to the eye’s light-sensing photoreceptors and provides them nourishment and support.
People with OCA lack pigmented RPE and have an underdeveloped fovea, an area within the retina that is crucial for central vision. The optic nerve carries visual signals to the brain.
People with OCA have misrouted optic nerve fibers. Scientists think that RPE plays a role in forming these structures and want to understand how lack of pigment affects their development.

“Animals used to study albinism are less than ideal because they lack foveae,” said NEI clinical director Dr. Brian P. Brooks, chief of the Ophthalmic Genetics and Visual Function Branch. “A human stem cell model that mimics the disease is an important step forward in understanding albinism and testing potential therapies to treat it.”
To make the model, researchers reprogrammed skin cells from individuals without OCA and people with the two most common types of OCA (OCA1A and OCA2) into pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). The iPSCs were then differentiated to RPE cells. The RPE cells from OCA patients were identical to RPE cells from unaffected individuals but displayed significantly reduced pigmentation.
Researchers will use the model to study how lack of pigmentation affects RPE physiology and function. In theory, if fovea development is dependent on RPE pigmentation, and pigmentation can be somehow improved, vision defects associated with abnormal fovea development could be at least partially resolved, according to Brooks.
“Treating albinism at a very young age, perhaps even prenatally, when the eye’s structures are forming, would have the greatest chance of rescuing vision,” said Brooks. “In adults, benefits might be limited to improvements in photosensitivity, for example, but children may see more dramatic effects.”
The team is now exploring how to use their model for high-throughput screening of potential OCA therapies.
